

Use the slider to adjust the values in the EMI calculator form. EMI in arrears OR EMI in advance (for car loan only).Principal loan amount you wish to avail (rupees).You can calculate EMI for home loan, car loan, personal loan, education loan or any other fully amortizing loan using this calculator.Įnter the following information in the EMI Calculator: With colourful charts and instant results, our EMI Calculator is easy to use, intuitive to understand and is quick to perform. Our EMI calculator automates this calculation for you and gives you the result in a split second along with visual charts displaying payment schedule and the break-up of total payment. The total amount payable will be ₹13,493 * 120 = ₹16,19,220 that includes ₹6,19,220 as interest toward the loan.Ĭomputing EMI for different combinations of principal loan amount, interest rates and loan term using the above EMI formula by hand or MS Excel is time consuming, complex and error prone. i.e., you will have to pay ₹13,493 for 120 months to repay the entire loan amount. (i.e., r = Rate of Annual interest/12/100. R is rate of interest calculated on monthly basis. Even though your monthly EMI payment won't change, the proportion of principal and interest components will change with time. With each successive payment, you'll pay more towards the principal and less in interest.
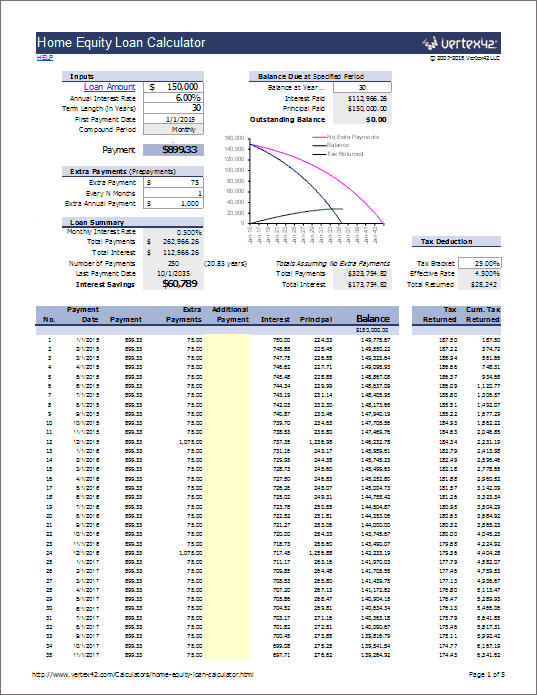
The exact percentage allocated towards payment of the principal depends on the interest rate. The interest component of the EMI would be larger during the initial months and gradually reduce with each payment. The sum of principal amount and interest is divided by the tenure, i.e., number of months, in which the loan has to be repaid. It consists of the interest on loan as well as part of the principal amount to be repaid.

Common types of unsecured loans include credit cards and student loans. Unsecured loans don’t require collateral, though failure to pay them may result in a poor credit score or the borrower being sent to a collections agency. In exchange, the rates and terms are usually more competitive than for unsecured loans. Common examples of secured loans include mortgages and auto loans, which enable the lender to foreclose on your property in the event of non-payment. Secured loans require an asset as collateral while unsecured loans do not.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
